Unveiling the Dark Secrets of Money Laundering Integration
Money laundering is one of the most dangerous crimes, undermining the economy and threatening businesses worldwide. To effectively combat this growing menace, it’s vital to grasp its process. The three stages—placement, layering, and integration—are at the heart of how illicit money is transformed. Among these, integration is the most critical and final stage, where dirty money becomes indistinguishable by blending into the legitimate economy, making it nearly impossible to trace.
For businesses, ignoring the implementation of anti-money laundering measures can lead to severe adverse impacts. Every missed opportunity to act allows these crimes to grow day by day, exposing companies to risks. In my professional experience, I’ve observed companies fail because they underestimated the importance of strong measures. Proactively developing advanced systems and safeguards is not just smart—it’s essential.
Although integration completes the laundering process, addressing placement and layering early can significantly minimize risks. Each business should invest in robust tools and processes to avoid becoming a target of these evolving schemes.
Exposing the Hidden Truths of Money Laundering
Money laundering is a sophisticated scheme used to conceal the origin of illicit funds. Criminals, often referred to as launderers, take dirty money and funnel it through a web of accounts, making it seem clean and legitimate. The process involves three critical stages: placement, where the money enters the system; layering, which involves disguising the funds through complex transactions; and integration, where the criminal proceeds are mixed with legitimate sources, effectively erasing their true origin. By the final stage, tracing the funds becomes a daunting task for authorities.
To prevent these activities, Anti-Money Laundering laws require businesses and specific professions to implement strict controls and measures. These customized systems focus on identifying associated risk indicators and understanding the operating cycle of laundering schemes. A regulated entity that fully grasps the concept and employs precise controls can effectively detect and stop these attempts. With strong regulations and vigilance, authorities aim to safeguard the system and limit the impact of such schemes on society and the economy.
Decoding the Critical Stages of Money Laundering: A Hidden Threat
Money laundering operates through three essential stages, each designed to disguise the origin of illicit funds.
Infiltrating the System: The Crucial Step of Placement
Placement, the first stage in this process, involves introducing illegally obtained money into legitimate financial systems. Criminals, or launderers, often rely on methods like smurfing and structuring, breaking large amounts of cash into smaller denominations to avoid detection. These smaller amounts are then deposited into multiple accounts under false names or at different locations. Additionally, they may purchase luxury items or real estate with cash, seamlessly embedding the illicit funds into the economy. This stage often takes place in the country where the funds originated or in another jurisdiction with weaker regulations, allowing criminals to exploit loopholes and avoid scrutiny.
Shrouding the Truth: The Strategic Art of Layering
The layering stage in money laundering is meant to hide the link between illegally obtained funds and their illegal source. During this phase, illegal money is moved through multiple layers of complex transactions, including the use of accounts, legal structures, and cross-border transactions. To make the trail harder to follow, criminals set up shell companies and shelf companies, masking ownership and complicating investigations. They also convert funds into complex financial instruments, further increasing the distance from their origin. By involving various parties and creating intricate pathways, these strategies make it incredibly challenging to trace the funds as they move through the economy.
Sealing the Deception: The Final Step of Integration
The integration stage is the last step in the money laundering process, where dirty funds are mingled with legitimate funds to erase their illegal origin. At this point, criminal proceeds are integrated into regular funds, making it hard for authorities to detect the illegal amount. These funds are then used for personal benefits or redirected into criminal activities without raising an inquiry. Understanding the intricacies of this stage is vital to prevent the completion of laundering and stop the flow of illegal money into the clean economy.
Unmasking the Final Act: Integration Stage and Its Hidden Techniques
The integration stage marks the end of the money laundering process, where dirty money undergoes seamless blending with legitimate earnings. This stage makes it hard for authorities to segregate illegal funds from their original source. Once the criminal proceeds are mixed with regular funds, criminals use them in routine courses, raising no suspicion. By disguising the funds’ origin, this stage ensures the laundered money appears clean and usable.
Unveiling the Hidden Purpose: Integration in Money Laundering
The integration stage is the final phase of the money laundering process, where launderers ensure the dirty money is mixed with legitimate funds. After enough layering to conceal the origin of illegal funds, the money is ready to be freely used. The primary purpose is to enable launderers to spend the funds on personal benefits or reinvest them in criminal activities without drawing attention from regulatory authorities. By blending the funds seamlessly, the launderer creates an illusion of legality, completing the laundering process.
Exposing the Deceptive Methods: Integration in Money Laundering
During the integration stage, criminals employ complex transactions involving multiple parties and bank accounts to disguise the source of illegal money. By creating a complicated trail of documentation, they make the funds look as though they come from legal sources. These carefully crafted techniques ensure the money is successfully integrated into legally generated income, allowing it to flow undetected into the financial system without raising any suspicion.
Transforming Crime to Credibility: Investing in Legitimate Ventures
Criminals often funnel illegally obtained funds into legitimate business activities to hide their source. Once the money is part of the business, it is presented as business profits, minimizing the likelihood of inquiries. By merging these funds into normal activities, they transform illegal money into what appears to be clean business capital, making it nearly impossible to uncover its criminal origins.
Turning Wealth into Power: The Allure of Real Estate and Assets
One common method to disguise illegal funds is by investing in real estate or buying luxurious items like yachts, expensive cars, antiques, or even cryptocurrencies. These assets are eventually sold to generate income, often labeled as a sale of assets, or used as collateral for loans from financial institutions. By creating a distance from the illegal source, criminals present the amounts as legitimate proceeds from selling property or similar assets. With the help of detailed documentation, they can avoid questions about how these high-end properties or funds were originally acquired.
Unveiling the Shadows: The Hidden World of Shell Companies and Offshore Accounts
Criminals often rely on shell companies, shelf companies, and offshore accounts during the integration stage to disguise funds. They set up an intricate network of legal structures spanning multiple jurisdictions, particularly in countries with lax regulatory requirements. These loopholes make it difficult for authorities to trace the true identity of the owner. Additionally, weak disclosure laws in these regions further obscure the origin and flow of the money, ensuring it remains hidden within a maze of paperwork and transactions.
Unmasking the Deception: The Dark Art of Trade-Based Money Laundering
Trade-based money laundering uses commercial transactions as a cover to hide illegal proceeds. Criminals manipulate invoices through over-invoicing or under-invoicing, often tied to a legitimate business, to move and mix dirty funds across borders. These schemes are backed by false documentation, allowing the money to change hands and flow through bank accounts without drawing suspicion. This creates a complex trail, making it incredibly challenging to uncover the source of the funds.
Exploiting Financial Tools: The Hidden Risks of Money Laundering
Criminals often use financial products, like life insurance policies, to disguise laundered sums. Launderers purchase multiple policies and sell them quickly, turning criminal proceeds into money labeled as funds generated from insurance. This method allows the illegal money to appear legitimate while avoiding detection.
Unraveling the Maze: The Daunting Complexities of Tracking Dirty Money
Tracking criminal proceeds during the integration stage of the money laundering process is a highly complex challenge for several reasons:
- First, the placement stage and layering stage involve numerous accounts and persons, effectively concealing the true mastermind behind the funds.
- Additionally, launderers frequently rely on foreign systems, and without international cooperation, tracing these funds across borders becomes nearly impossible.
- Furthermore, tools like nominee arrangements, shell companies, and a complex chain obscure the source of illegal money, complicating investigations.
- Lastly, through careful planning and limited value transactions, the criminal funds appear natural and reasonable, evading detection by authorities.
Defending Integrity: Essential Measures to Detect and Prevent Money Laundering Attempts
Authorities worldwide have created laws and regulations to fight money laundering and other financial crimes. These rules help regulated entities, such as legitimate businesses in the financial sector, to apply strong controls and effective processes. Moreover, these measures aim to prevent misuse of systems and ensure compliance with AML regulations, protecting the economy from exploitation.
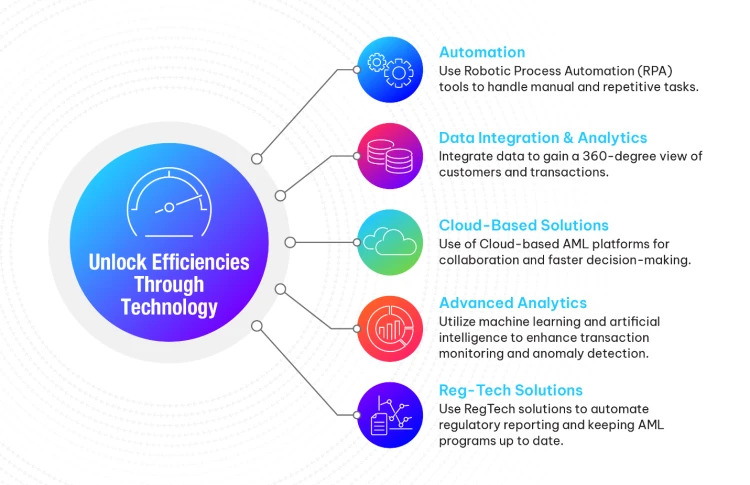
A strong anti-money laundering Program includes carefully designed systems and focused mitigation measures. Additionally, continuous efforts are made to detect and stop illegal activities at all money laundering stages. By identifying vulnerabilities and fixing loopholes, these entities can create a secure system that prevents risks and preserves integrity.
Protecting Trust and Transparency: The Power of Customer Due Diligence
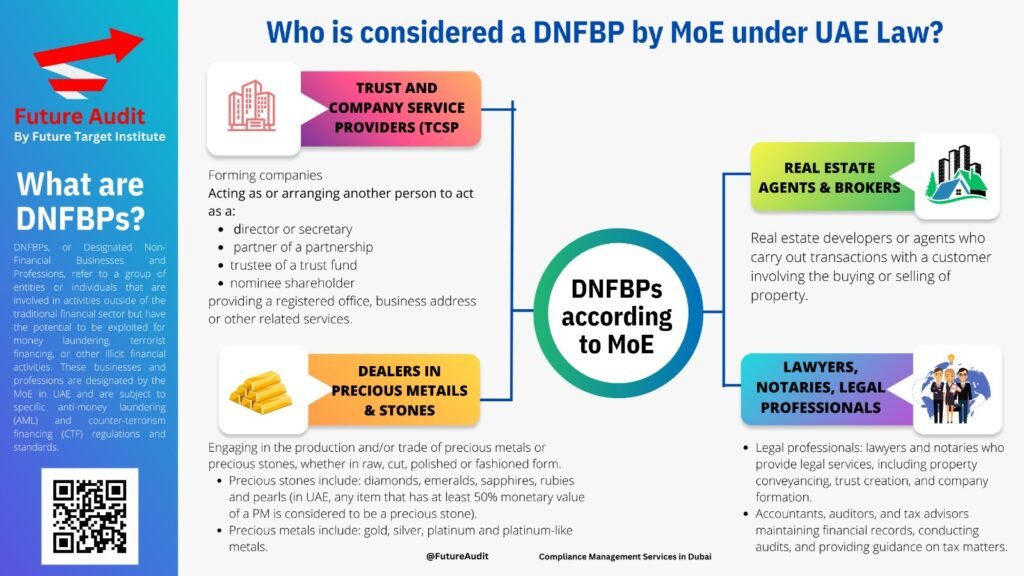
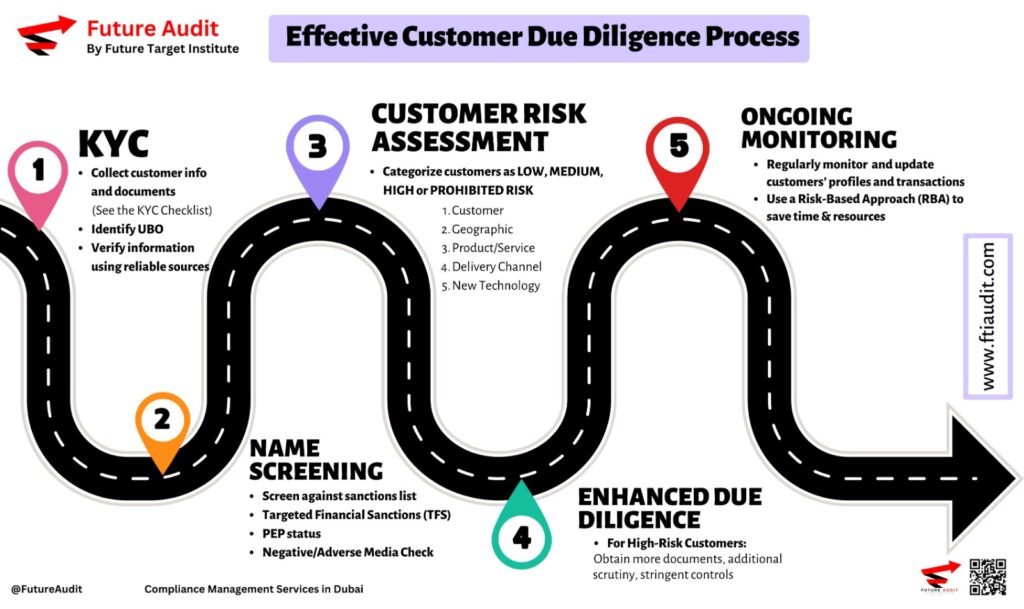
Regulated entities must implement Customer Due Diligence (CDD) to confirm the legitimacy of identities and analyze business relationships. Additionally, they should examine the legal structure and identify beneficial owners to maintain complete transparency. Furthermore, both prospects and existing customers need to be screened for ties to sanctioned individuals, Politically Exposed Persons, or criminal activities. Based on this information, entities develop a customer’s risk profile to determine their level of risk to the business. For higher-risk customers, an Enhanced Due Diligence process is crucial to fight money laundering and associated threats.
Empowering Employees: The Vital Role of AML Training in Safeguarding Integrity
AML training is essential for employees to understand their role in preventing money laundering. By implementing a strong AML framework, with clear procedures and controls, employees can spot suspicious activities and protect customer information. Compliance Officers guide the organization structure to ensure AML policies are followed. This helps regulated entities identify potential risk indicators. As a result, AML training stops money launderers from exploiting the business and protects legal financial systems from ill-gotten funds.
How AML UAE Can Empower Your Fight Against Money Laundering: Unmatched Support and Expertise
AML UAE plays a crucial role in the fight against money laundering by guiding regulated entities at every step. Our professional consultants help businesses assess their exposure to illegal funds and customize AML policies to suit their needs. We provide AML training to both teams and compliance officers, ensuring they can spot suspicious indicators and know exactly what actions to take when red flags appear. Using Enterprise-Wide Risk Assessment (EWRA), we focus on effective implementation of ongoing measures to prevent the integration of illicit funds into the legitimate economy. Our personalized approach makes sure businesses are well-prepared to tackle money laundering and safeguard their operations.
FAQs
1. What is AML system integration?
AML system integration combines anti-money laundering tools with existing systems to detect and prevent suspicious activities. It helps monitor transactions, identify risks, and ensure compliance with AML regulations.
2. How does AML UAE help businesses in preventing money laundering?
AML UAE offers expert consultants to help businesses assess exposure to illegal funds. They customize AML policies and provide AML training for staff and compliance officers to detect suspicious indicators.
3. What are the key stages of money laundering?
Money laundering happens in three stages: placement, where illegal funds enter the system; layering, where the origin is hidden; and integration, where funds are made to look legitimate.
4. Why is Customer Due Diligence (CDD) important in AML practices?
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) is essential to verify customer identities and assess potential risks. It helps businesses spot suspicious activities and comply with AML regulations.
5. What role does employee training play in AML prevention?
AML training is key to helping employees recognize suspicious activities. It ensures they can act on red flags and protect the business from money laundering risks.
6. How does AML UAE ensure businesses comply with AML regulations?
AML UAE offers consultancy, AML training, and ongoing support to ensure compliance. They help businesses implement effective AML measures, including Enterprise-Wide Risk Assessments.
7. What are the consequences of failing to implement AML measures?
Failing to implement AML measures can result in fines, reputational damage, and legal consequences. It may also enable money laundering and financial crimes.
8. How can businesses detect suspicious activities?
Businesses detect suspicious activities by using AML systems that flag unusual transactions. Monitoring transaction details and suspicious indicators helps identify threats early.
9. What is the importance of having a robust AML framework?
A strong AML framework includes policies, procedures, and controls to fight money laundering. It protects businesses from financial crimes and legal risks.
10. What does “Enterprise-Wide Risk Assessment” (EWRA) involve in AML?
Enterprise-Wide Risk Assessment (EWRA) evaluates a business’s vulnerability to money laundering. It helps assess risks, identify exposure to illegal funds, and implement AML controls.