One of the UAE’s strategic goals in combatting money laundering is to deepen the understanding of risk. This involves conducting comprehensive risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities and emerging trends in money laundering and terrorist financing activities. By gaining a deeper understanding of these risks, the UAE can develop targeted measures to mitigate them effectively.
Additionally, the UAE aims to improve its law enforcement capabilities in tackling money laundering. This includes enhancing the investigative and intelligence-gathering capabilities of its law enforcement agencies, such as the police and financial intelligence units. By equipping these agencies with the necessary tools and resources, the UAE can effectively detect, investigate, and prosecute money laundering cases, thereby deterring criminals from using its financial system for illicit activities.
Another strategic goal of the UAE is to enhance the effectiveness of supervisory efforts. This involves strengthening the regulatory framework and oversight mechanisms governing financial institutions and designated non-financial businesses and professions. The UAE’s regulatory authorities, such as the Central Bank and the Financial Services Regulatory Authority, work closely with these entities to ensure compliance with anti-money laundering and counter-terrorist financing regulations.
Furthermore, the UAE recognizes the importance of international cooperation in combatting money laundering. The country actively participates in global initiatives and collaborates with international organizations, such as the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), to align its efforts with international standards and best practices. Through these partnerships, the UAE can exchange information, share intelligence, and coordinate investigations, thereby strengthening its ability to combat cross-border money laundering and terrorist financing activities.
In conclusion, the UAE’s strategic goals in combatting money laundering revolve around deepening the understanding of risk, improving law enforcement capabilities, enhancing supervisory efforts, and fostering international cooperation. By pursuing these goals, the UAE is committed to safeguarding its financial system and protecting it from abuse by criminals and terrorists.
Understanding the Strategic Goals
The strategic goals of the UAE in combatting money laundering and terrorist financing are multi-faceted. They aim to:
- Deepen the understanding of risk
- Increase the standing of the Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU) within the UAE’s national AML/CFT framework
- Improve law enforcement authorities’ capabilities in detecting and investigating money laundering
- Use provisional and confiscation measures more frequently and effectively
- Accurately prosecute money laundering cases and apply proportionate and effective sanctions
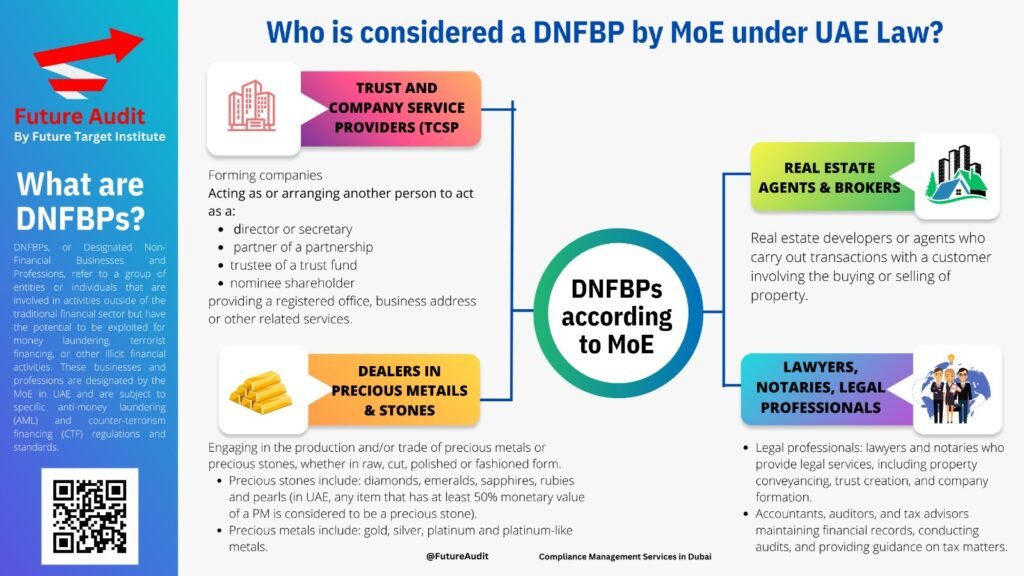
- Enhance the effectiveness of supervisor efforts for financial institutions and designated non-financial businesses and professions (DNFBPs)
- Identify and intercept unlicensed money remittance services
- Enhance the implementation of targeted financial sanctions without delay
- Align company registration frameworks across the UAE
- Strengthen the level of assistance the UAE provides to international partners
- Continue to effectively investigate, prosecute, and convict terrorist financing offenses
- Continue to modernize the UAE’s legal framework
- Establish a comprehensive public education and awareness program
Deepening the Understanding of Risk
One of the key goals of the UAE in combatting money laundering is to deepen the understanding of risk. This involves conducting thorough risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities and develop targeted strategies to mitigate those risks.
By analyzing the various sectors and industries that are more susceptible to money laundering, the UAE can focus its efforts on implementing preventive measures and enhancing supervision in those areas. This includes sectors such as banking and finance, real estate, precious metals and stones, and the non-profit sector.
For example, within the banking and finance sector, the UAE has implemented stringent regulations to ensure the transparency of financial transactions. Financial institutions are required to conduct due diligence on their customers and report any suspicious activities to the relevant authorities. Additionally, the UAE Central Bank has established a Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU) to collect, analyze, and disseminate financial intelligence to combat money laundering and terrorist financing.
In the real estate sector, the UAE has implemented measures to prevent money laundering through property transactions. The government requires individuals and entities involved in real estate transactions to verify the source of funds and report any suspicious transactions to the authorities. This helps to ensure that the real estate sector is not used as a means to launder illicit funds.
Similarly, the UAE has implemented regulations to prevent money laundering in the precious metals and stones industry. Dealers and traders in this sector are required to maintain detailed records of their transactions and report any suspicious activities to the relevant authorities. This helps to track the movement of precious metals and stones and detect any potential money laundering activities.
The non-profit sector is also a focus area for the UAE in combatting money laundering. The government has implemented regulations to ensure that non-profit organizations are not used as a front for money laundering or terrorist financing. Non-profit organizations are required to maintain transparent financial records and report any suspicious activities to the authorities.
Furthermore, the UAE aims to collaborate with international partners to share information and best practices in identifying and addressing emerging money laundering risks. This collaboration allows for the exchange of knowledge and expertise, enabling the UAE to stay updated on the latest trends and techniques used by money launderers.
Through these efforts, the UAE is working towards deepening its understanding of risk and implementing effective measures to combat money laundering. By targeting vulnerable sectors and industries, implementing stringent regulations, and collaborating with international partners, the UAE is taking a proactive approach in safeguarding its financial system and maintaining its reputation as a global financial hub.
To achieve this goal, the UAE government has implemented various initiatives and programs. One such initiative is the establishment of specialized training centers for law enforcement officers. These centers offer comprehensive courses on money laundering detection and investigation techniques, equipping officers with the necessary skills and knowledge to effectively combat this financial crime. Additionally, the UAE has also strengthened its collaboration with international law enforcement agencies and financial intelligence units. Through information sharing and joint operations, authorities can better track and identify cross-border money laundering activities. This collaboration not only enhances the investigative capabilities of UAE law enforcement but also contributes to global efforts in combating money laundering and terrorist financing. Furthermore, the UAE has implemented stricter regulations and guidelines for financial institutions and other entities susceptible to money laundering risks. These regulations require enhanced due diligence measures, customer identification procedures, and the implementation of robust internal controls to detect and report suspicious transactions. By holding these entities accountable and ensuring compliance, the UAE aims to create a more transparent and secure financial system. In line with its commitment to enhancing the use of provisional and confiscation measures, the UAE has enacted legislation that empowers authorities to freeze and seize assets suspected to be linked to money laundering or other illicit activities. This legislation also provides a legal framework for the confiscation and forfeiture of these assets, ensuring that criminals are deprived of the proceeds of their illegal activities. Moreover, the UAE has established specialized units within its law enforcement agencies dedicated to investigating money laundering cases. These units are staffed with highly trained officers who possess expertise in financial analysis, forensic accounting, and digital investigations. By leveraging advanced technologies and specialized skills, these units can effectively trace illicit funds, identify money laundering techniques, and gather robust evidence for successful prosecutions. Overall, the UAE’s efforts to improve law enforcement authorities’ capabilities in combating money laundering are comprehensive and multi-faceted. Through specialized training, international collaboration, stricter regulations, and the use of provisional and confiscation measures, the UAE is determined to disrupt the financial networks of criminals and safeguard its financial system from the threats posed by money laundering.In addition to regular inspections and assessments, the UAE is also focused on improving the quality and depth of its supervisory processes. This includes enhancing the skills and capabilities of supervisors through specialized training programs and workshops.
Supervisors are being equipped with the necessary tools and knowledge to effectively identify emerging risks and trends in money laundering and terrorist financing activities. By staying up-to-date with the latest techniques and methodologies used by criminals, supervisors can better understand the evolving nature of financial crimes and develop proactive measures to combat them.
Furthermore, the UAE is actively promoting information sharing and collaboration among supervisors, both domestically and internationally. Recognizing that money laundering and terrorist financing are global issues, the UAE understands the importance of working together with other jurisdictions to combat these threats.
Through various mechanisms such as bilateral agreements, information exchange platforms, and participation in international organizations, the UAE is fostering a culture of cooperation and coordination among supervisors. This allows for the sharing of best practices, intelligence, and expertise, ultimately leading to more effective supervision and a stronger global AML/CFT regime.
Moreover, the UAE is leveraging technology to enhance its supervisory efforts. By harnessing the power of data analytics and artificial intelligence, supervisors can analyze vast amounts of financial data in real-time, enabling them to detect suspicious transactions and patterns more efficiently.
Advanced technologies such as machine learning algorithms and predictive analytics are being employed to identify potential money laundering and terrorist financing activities before they can cause significant harm. This proactive approach not only strengthens the UAE’s supervisory framework but also acts as a deterrent to criminals who may be considering using the country’s financial system for illicit purposes.
Overall, the UAE’s commitment to enhancing supervisory efforts is evident in its comprehensive and holistic approach. By prioritizing higher-risk sectors, investing in the skills and capabilities of supervisors, promoting information sharing and collaboration, and leveraging technology, the UAE is well-positioned to effectively combat money laundering and terrorist financing and maintain the integrity of its financial system.
Aligning company registration frameworks across the UAE is a crucial step in the country’s ongoing fight against money laundering and illicit financial activities. Currently, different emirates in the UAE have their own registration processes and requirements, which can create inconsistencies and loopholes that can be exploited by criminals.
By standardizing the registration process, the UAE can ensure that all companies, regardless of their location within the country, are subject to the same rigorous scrutiny and due diligence measures. This will help eliminate any potential weak points in the system and make it more difficult for illicit actors to abuse the corporate structure for money laundering purposes.
One of the key aspects of aligning company registration frameworks is the focus on beneficial ownership transparency. Beneficial ownership refers to the individuals who ultimately own or control a company, even if their names are not listed on official documents. This information is crucial for law enforcement agencies and financial institutions to identify and investigate any suspicious activities.
Under the aligned registration frameworks, companies will be required to disclose their beneficial owners, providing a comprehensive and accurate picture of the individuals behind the corporate entities. This will greatly enhance the traceability of funds and assets, making it easier to identify and prevent money laundering schemes.
In addition to beneficial ownership transparency, the aligned registration frameworks will also introduce stricter due diligence measures. This means that companies will be required to provide more detailed information about their business activities, sources of funds, and the nature of their operations. By collecting this information, authorities can better assess the legitimacy of the company and identify any potential red flags.
Furthermore, the aligned frameworks will also incorporate enhanced monitoring and reporting mechanisms. Companies will be required to regularly update their registration information and report any significant changes in their ownership structure or business operations. This will ensure that the authorities have access to up-to-date and accurate information, enabling them to detect and investigate any suspicious activities in a timely manner.
Overall, aligning company registration frameworks across the UAE is a crucial step towards creating a more transparent and robust corporate environment. By implementing consistent and stringent registration requirements, the UAE is sending a strong message that it is committed to combating money laundering and illicit financial activities. This will not only protect the integrity of the country’s financial system but also contribute to the global efforts in the fight against money laundering and terrorist financing.
One key aspect of modernizing the legal framework is the implementation of comprehensive risk assessment mechanisms. These mechanisms allow authorities to identify and assess the potential risks associated with money laundering and terrorist financing activities. By understanding the specific vulnerabilities and threats faced by the UAE, policymakers can develop targeted strategies and measures to mitigate these risks.
Moreover, the UAE recognizes the importance of enhancing its regulatory framework to keep pace with technological advancements. As financial transactions increasingly occur online and through digital platforms, it is crucial to establish effective regulations that address the unique challenges posed by these emerging technologies. This includes adopting robust cybersecurity measures to protect against cyber-enabled financial crimes.
Furthermore, the UAE is committed to promoting transparency and accountability in its financial system. This involves implementing measures to enhance the identification and verification of beneficial owners of legal entities and ensuring that financial institutions adhere to stringent know-your-customer (KYC) and anti-money laundering (AML) procedures. By strengthening these procedures, the UAE can effectively detect and prevent the misuse of its financial system for illicit activities.
Additionally, the UAE recognizes the importance of international cooperation in combating money laundering and terrorist financing. The country actively participates in global initiatives and works closely with international organizations such as the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) and the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC). Through these partnerships, the UAE can exchange information, expertise, and best practices with other countries, fostering a collective effort to combat financial crimes on a global scale.
In conclusion, the UAE’s commitment to modernizing its legal framework demonstrates its proactive approach in combating money laundering and terrorist financing. By continuously reviewing and updating its laws and regulations, strengthening risk assessment mechanisms, embracing technological advancements, promoting transparency, and fostering international cooperation, the UAE is well-positioned to effectively tackle the challenges posed by financial crimes in the modern era.
6. How does the UAE collaborate with international partners in combatting money laundering?
The UAE recognizes the importance of international cooperation in combatting money laundering and terrorist financing. It actively engages in information sharing and mutual legal assistance with other countries to investigate and prosecute cross-border financial crimes. The UAE also participates in international initiatives and organizations, such as the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), to exchange best practices and contribute to the development of global AML/CFT standards.
7. What measures does the UAE take to raise public awareness about money laundering?
The UAE places great emphasis on raising public awareness about the risks and consequences of money laundering. It conducts educational campaigns, workshops, and seminars to educate individuals, businesses, and organizations about the importance of complying with AML/CFT regulations. The government also works closely with the media to disseminate information and promote a culture of reporting suspicious financial activities.
8. How does the UAE ensure the integrity of its financial system?
The UAE has implemented a robust regulatory framework to ensure the integrity of its financial system. It requires financial institutions to establish comprehensive customer due diligence procedures, conduct ongoing monitoring of customer transactions, and report any suspicious activities to the relevant authorities. The UAE Central Bank and other regulatory bodies regularly conduct inspections and audits to ensure compliance with AML/CFT regulations.
9. What penalties are imposed for money laundering in the UAE?
The UAE has stringent penalties for money laundering offenses. Individuals convicted of money laundering can face imprisonment, fines, and confiscation of assets. The severity of the penalties depends on the nature and extent of the offense. The UAE’s legal system also allows for the extradition of individuals involved in money laundering to face justice in the country.
10. How does the UAE promote international investment while combatting money laundering?
The UAE recognizes the importance of promoting international investment while maintaining a strong AML/CFT regime. It has implemented measures to streamline the process of setting up businesses and investing in the country, while ensuring compliance with AML/CFT regulations. The UAE’s commitment to transparency and robust supervision helps build trust among international investors, who recognize the country as a safe and secure destination for their investments.