Who is Considered a DNFBP by MOE under UAE Law?
In the United Arab Emirates (UAE), the Ministry of Economy (MOE) plays a crucial role in regulating and supervising the activities of Designated Non-Financial Businesses and Professions (DNFBPs). DNFBPs are entities that are involved in activities that have the potential to be exploited for money laundering or terrorist financing purposes. In this article, we will explore who is considered a DNFBP under UAE law and the responsibilities and obligations that come with this designation.
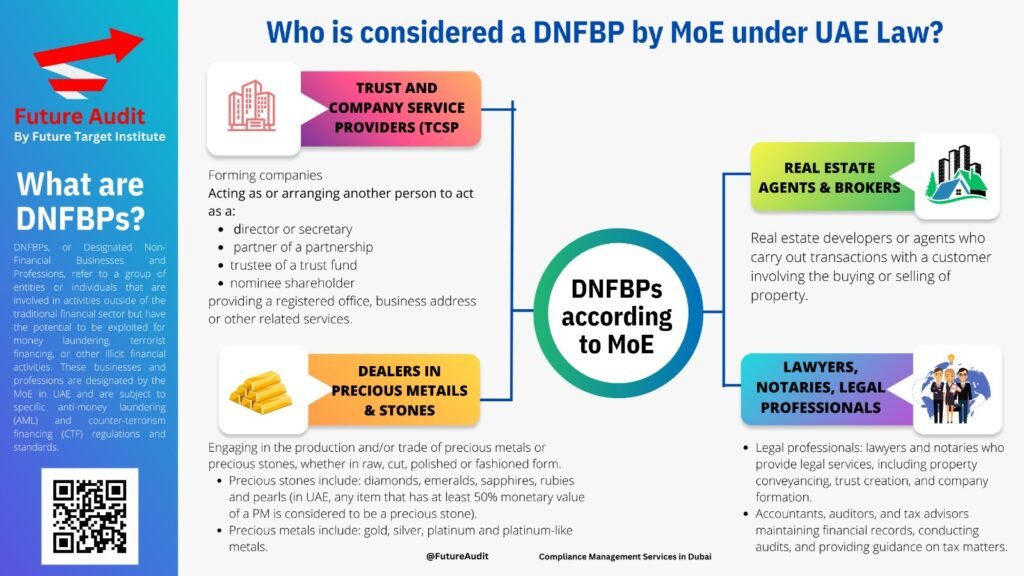
Under UAE law, several types of businesses and professions are considered DNFBPs. These include real estate agents, dealers in precious metals and gemstones, lawyers, notaries, and other independent legal professionals, accountants, auditors, and tax advisors, trust and company service providers, and casinos. These entities are deemed to be vulnerable to money laundering and terrorist financing due to the nature of their activities and the potential for anonymity and large financial transactions.
Real estate agents, for example, are included in the DNFBP category because they often deal with high-value transactions and have access to significant amounts of funds. This makes them attractive targets for money laundering activities. Similarly, dealers in precious metals and gemstones are included as they handle valuable assets that can be easily converted into cash, making them susceptible to illicit financial activities.
Lawyers, notaries, and other independent legal professionals are also considered DNFBPs due to their role in facilitating financial transactions and providing legal services. They may be involved in activities such as creating and managing trusts, establishing companies, and handling large sums of money on behalf of their clients. This places them at risk of being exploited for money laundering or terrorist financing purposes.
Accountants, auditors, and tax advisors are included in the DNFBP category because they have access to financial information and play a crucial role in ensuring compliance with tax laws and regulations. Their involvement in financial transactions and their knowledge of financial systems make them potential targets for money laundering activities.
Trust and company service providers are also considered DNFBPs as they assist in the creation and management of trusts and companies. They may be involved in activities such as providing nominee services, acting as registered agents, or offering corporate secretarial services. These services can be misused for illicit purposes, making them subject to regulatory scrutiny.
Casinos, with their large cash flows and potential for anonymity, are also included in the DNFBP category. The nature of their business makes them susceptible to money laundering and terrorist financing activities. The UAE has implemented strict regulations and controls to ensure that casinos are not misused for illicit financial activities.
Being designated as a DNFBP comes with significant responsibilities and obligations. These entities are required to implement robust anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorist financing (CTF) measures to detect and prevent illicit financial activities. They must conduct thorough customer due diligence, monitor transactions, and report any suspicious activities to the relevant authorities.
The MOE, along with other regulatory bodies in the UAE, conducts regular inspections and audits to ensure compliance with AML and CTF regulations. Non-compliance can result in severe penalties, including fines, suspension of business activities, or even criminal prosecution.
In conclusion, DNFBPs in the UAE, such as real estate agents, lawyers, accountants, and casinos, play a vital role in the economy but are also vulnerable to money laundering and terrorist financing activities. The MOE’s oversight and regulation of these entities are essential to safeguard the integrity of the financial system and protect against illicit financial activities.
Trust and Company Service Providers (TCSP)
One category of DNFBPs identified by the MOE is Trust and Company Service Providers (TCSPs). TCSPs are entities that provide services related to the formation and administration of trusts and companies. This includes acting as or arranging for another person to act as a director or secretary, a partner of a partnership, a trustee of a trust fund, or a nominee shareholder. TCSPs also offer services such as providing a registered office, business address, or other related services.
TCSPs play a crucial role in facilitating business activities and financial transactions globally. They act as intermediaries between individuals or companies and the legal entities they wish to establish or manage. These service providers ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, maintain corporate records, and ensure the smooth operation of trusts and companies. The services offered by TCSPs are diverse and tailored to meet the specific needs of their clients. They assist in the formation and registration of companies, including the preparation of necessary legal documents and the filing of required forms with the relevant authorities. TCSPs also provide administrative support by acting as directors or secretaries of companies, handling correspondence, and maintaining statutory records. In addition to company formation and administration, TCSPs offer services related to trusts. They assist in the establishment of trusts, ensuring compliance with trust laws and regulations. TCSPs may act as trustees or nominate individuals or entities to act as trustees on behalf of their clients. They handle the day-to-day administration of trusts, including the management of trust assets, distribution of funds, and compliance with legal obligations. Furthermore, TCSPs provide registered office and business address services, allowing companies to establish a physical presence in different jurisdictions. This is particularly useful for businesses operating internationally or seeking to expand their operations globally. TCSPs offer professional office spaces, mail forwarding services, and telephone answering services, enabling companies to maintain a local presence without the need for a physical office. The role of TCSPs in the global economy cannot be understated. They contribute to the ease of doing business by providing essential support services to individuals and companies. TCSPs also play a crucial role in ensuring transparency and compliance with anti-money laundering and counter-terrorism financing regulations. They are required to implement robust due diligence measures, conduct ongoing monitoring of clients, and report suspicious activities to the relevant authorities. Given the nature of their services, TCSPs are subject to regulatory oversight and licensing requirements in many jurisdictions. Governments and regulatory bodies have implemented measures to ensure that TCSPs adhere to high standards of professionalism, integrity, and transparency. This includes conducting background checks on individuals involved in TCSP activities, imposing reporting obligations, and conducting periodic audits to assess compliance with regulatory requirements. In conclusion, Trust and Company Service Providers (TCSPs) are indispensable entities in the global business landscape. They provide a wide range of services related to the formation and administration of trusts and companies, ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. TCSPs play a vital role in facilitating business activities, maintaining corporate records, and promoting transparency in financial transactions. Their services contribute to the smooth operation of businesses and the global economy as a whole.Responsibilities and Obligations of TCSPs
As DNFBPs, TCSPs have certain responsibilities and obligations that they must fulfill to ensure compliance with UAE law and regulations. These include:
1. Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CTF) Measures
TCSPs are required to implement robust AML and CTF measures to prevent their services from being misused for illicit purposes. This includes conducting customer due diligence (CDD) procedures to verify the identity of their clients, assessing and mitigating the risks associated with their services, and reporting any suspicious transactions to the relevant authorities.
Furthermore, TCSPs must also establish and maintain a comprehensive AML and CTF program that outlines their policies, procedures, and controls for detecting and preventing money laundering and terrorist financing. This program should be regularly reviewed and updated to ensure its effectiveness in addressing evolving risks and regulatory requirements.
2. Record-Keeping
TCSPs must maintain accurate and up-to-date records of their clients, including their identification documents, transaction records, and any other relevant information. These records should be readily accessible and retained for a specified period as prescribed by the UAE authorities.
Additionally, TCSPs should have proper systems in place to monitor and track client transactions, ensuring that they are able to provide timely and accurate information to the authorities when requested. This includes maintaining records of the source of funds and the purpose of transactions, as well as any additional information that may be required to establish the legitimacy of the transactions.
3. Internal Controls and Training
TCSPs are expected to establish and maintain effective internal controls to detect and prevent money laundering and terrorist financing activities. This includes implementing policies and procedures, conducting regular risk assessments, and providing ongoing training to their employees to ensure they are aware of their obligations and can effectively identify and report suspicious activities.
Furthermore, TCSPs should have a designated compliance officer responsible for overseeing the implementation of AML and CTF measures and ensuring compliance with applicable laws and regulations. This individual should have the necessary expertise and authority to carry out their duties effectively.
4. Reporting Obligations
If a TCSP becomes aware or has reasonable grounds to suspect that a transaction or activity is related to money laundering or terrorist financing, they are obligated to promptly report this information to the UAE Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU). Failure to report such information may result in severe penalties and legal consequences.
TCSPs should have clear procedures in place for reporting suspicious transactions, including the documentation and retention of relevant information. They should also maintain open lines of communication with the FIU and other relevant authorities to facilitate the reporting process and ensure timely and accurate information exchange.
In conclusion, TCSPs play a crucial role in the UAE’s efforts to combat money laundering and terrorist financing. By fulfilling their responsibilities and obligations, TCSPs contribute to the integrity of the financial system and help maintain the UAE’s reputation as a safe and transparent jurisdiction for business and investment.
Real Estate Agents
Another category of DNFBPs identified by the MOE is real estate agents. Real estate agents play a significant role in facilitating property transactions and are therefore susceptible to being exploited for money laundering purposes. Under UAE law, real estate agents are considered DNFBPs and are subject to specific obligations and regulations.
Real estate agents in the UAE are required to adhere to stringent anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorism financing (CTF) regulations. These regulations aim to prevent the real estate sector from being used as a means to launder illicit funds or finance terrorist activities. To ensure compliance, real estate agents are obligated to implement robust customer due diligence (CDD) measures. This includes conducting thorough background checks on clients, verifying their identities, and assessing the source of their funds. Additionally, agents must maintain comprehensive records of all transactions, including supporting documentation such as contracts, proof of ownership, and financial statements. Furthermore, real estate agents are required to report any suspicious transactions or activities to the relevant authorities. This not only helps in detecting and preventing money laundering but also contributes to the overall efforts in combating financial crime. The UAE government has established a dedicated Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU) to receive and analyze these reports, ensuring effective enforcement of AML and CTF regulations. In addition to these obligations, real estate agents are also subject to ongoing training and awareness programs. These programs aim to educate agents about the latest AML and CTF trends, typologies, and best practices. By staying informed and updated, agents can better identify potential risks and take appropriate measures to mitigate them. The role of real estate agents in the UAE’s AML framework cannot be understated. They act as gatekeepers, ensuring that the real estate sector remains transparent and free from illicit activities. By diligently adhering to their obligations and regulations, real estate agents contribute to maintaining the integrity and reputation of the UAE’s real estate market. It is worth noting that the UAE’s efforts in combating money laundering and terrorist financing in the real estate sector are in line with international standards and best practices. The country is an active participant in global initiatives, such as the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), and continuously reviews and enhances its AML and CTF framework to stay ahead of evolving threats. In conclusion, real estate agents in the UAE have a crucial role in preventing money laundering and terrorist financing. Through their compliance with AML and CTF regulations, these agents contribute to maintaining the integrity of the real estate sector and safeguarding the country’s financial system. The stringent obligations and regulations imposed on real estate agents reflect the UAE’s commitment to combat financial crime and ensure a secure and transparent business environment.4. Record Keeping
In addition to the above responsibilities, real estate agents are also required to maintain accurate and up-to-date records of their transactions and client information. This includes keeping records of all CDD documentation, suspicious transaction reports, and any other relevant information. These records must be retained for a specified period of time, as determined by the regulatory authorities.
5. Risk Assessment
Real estate agents must conduct regular risk assessments to identify and assess the potential money laundering and terrorist financing risks associated with their business activities. This involves considering factors such as the nature of their clients, the types of transactions they engage in, and the geographical locations in which they operate. Based on the results of these assessments, real estate agents must implement appropriate measures to mitigate and manage these risks.
6. Training and Awareness
To ensure compliance with their obligations, real estate agents must provide training to their employees on AML and CTF measures. This training should cover topics such as recognizing and reporting suspicious activities, understanding the legal and regulatory requirements, and implementing effective internal controls. By providing ongoing training and raising awareness among their employees, real estate agents can enhance their ability to detect and prevent money laundering and terrorist financing activities.
7. Cooperation with Authorities
Real estate agents are expected to cooperate fully with the relevant authorities in their efforts to combat money laundering and terrorist financing. This includes providing information and documentation as requested, responding to inquiries in a timely manner, and assisting with any investigations or enforcement actions. By cooperating with the authorities, real estate agents can contribute to the overall effectiveness of the AML and CTF framework.
8. Continuous Monitoring and Review
Real estate agents must continuously monitor their business relationships and transactions to detect any changes or red flags that may indicate potential money laundering or terrorist financing activities. This includes monitoring for any unusual or suspicious patterns of behavior, conducting periodic reviews of client information, and staying updated on the latest trends and typologies in money laundering and terrorist financing. By maintaining a proactive and vigilant approach, real estate agents can better protect themselves and their clients from the risks associated with financial crime.
In summary, real estate agents have a range of responsibilities and obligations when it comes to anti-money laundering and counter-terrorist financing measures. By fulfilling these obligations, real estate agents can contribute to the overall integrity and security of the real estate sector, and help prevent their services from being misused for illicit purposes.