

How to Remain Compliant with Sanctions Screening Requirements in the UAE
By Future Compliance | FTIAudit.com
Sanctions screening is a critical component of the UAE’s Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CTF) framework. Businesses operating in regulated sectors must comply with sanctions lists, financial restrictions, and asset freeze measures to avoid severe penalties, reputational damage, and potential legal action.
This guide provides an actionable approach to remaining compliant with sanctions screening requirements in the UAE.
What is Sanctions Screening?
Sanctions screening is the process of verifying customers, transactions, and business partners against international and UAE-specific sanctions lists to detect and prevent dealings with sanc
tioned individuals or entities.
Key authorities overseeing sanctions compliance in the UAE include:
UAE Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU)
Executive Office for Control and Non-Proliferation (EOCN)
Central Bank of UAE (CBUAE)
United Nations Security Council (UNSC) Sanctions Committees
Official UAE sanctions compliance portal
Step 1: Understanding Sanctions Lists
Businesses must screen against multiple sanctions lists, including:
1.UAE Local Terrorist List – Issued by the UAE Cabinet.
2.United Nations Security Council (UNSC) Sanctions List – Includes global restrictions on individuals, entities, and states.
3. OFAC (Office of Foreign Assets Control) List – U.S. Treasury Department’s sanctions.
4. EU & UK Sanctions Lists – Restrictions imposed by European authorities.
5. Other Regional Sanctions – GCC and FATF-related restrictions.


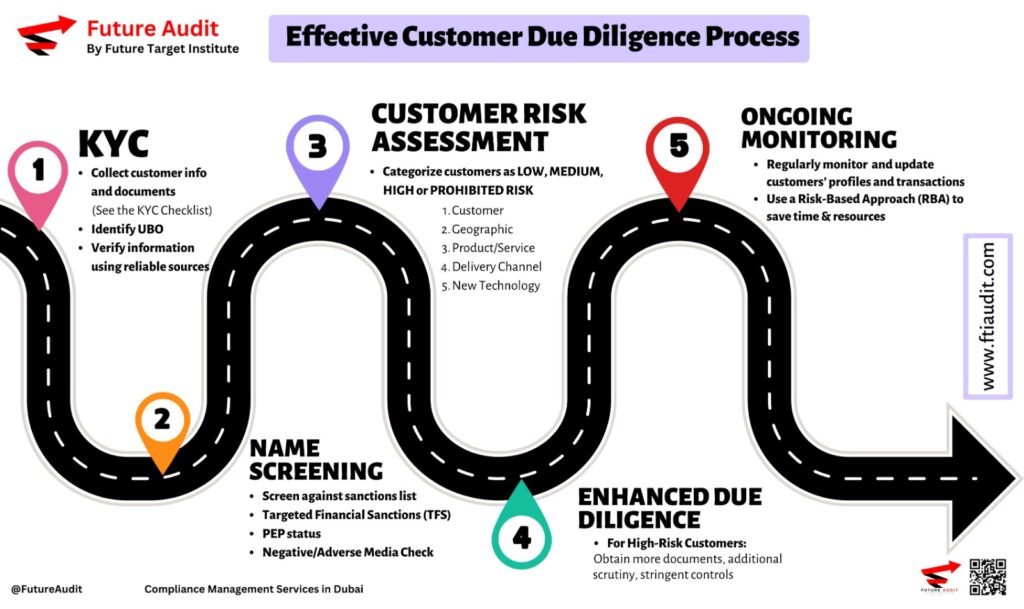
Step 2: Implementing an Effective Sanctions Screening Process
1. Conduct Regular Customer & Transaction Screening
Use automated sanctions screening tools to check customer names and transactions against updated sanctions lists.
Conduct screening at key touchpoints: onboarding, periodic reviews, and transaction execution.
Monitor high-risk industries such as finance, real estate, trade, and crypto assets.
2. Maintain Up-to-Date Sanctions Lists
Subscribe to real-time updates from UAE and international authorities.
Regularly update internal databases with newly designated sanctioned entities.
UAE FIU sanctions list updates
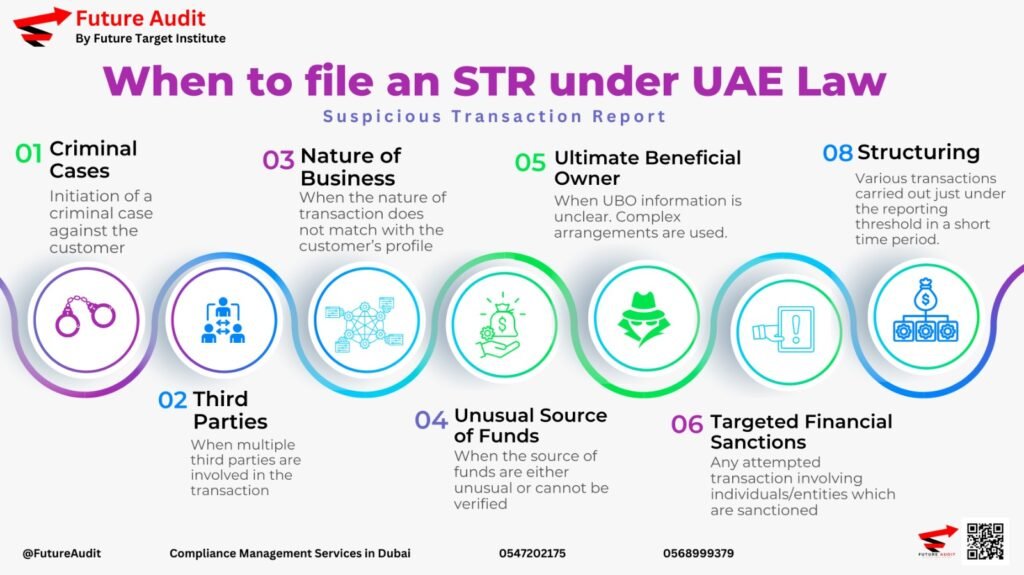
3. Report Matches & Freeze Assets Immediately
If a match is identified, report it to the UAE FIU via GoAML within 24 hours.
If required, freeze funds and assets linked to sanctioned individuals/entities.
Notify the Executive Office for Control & Non-Proliferation (EOCN) for guidance on handling frozen assets.
4. Train Your Compliance Team & Staff
Conduct mandatory AML and sanctions training for employees.
Provide role-specific guidance for compliance officers, front-line staff, and management.
Leverage UAE FIU’s free training resources.
Get Training from Future Compliance
Step 3: Essential Elements of an Effective Sanctions Screening Program
Regulatory Requirements & Compliance
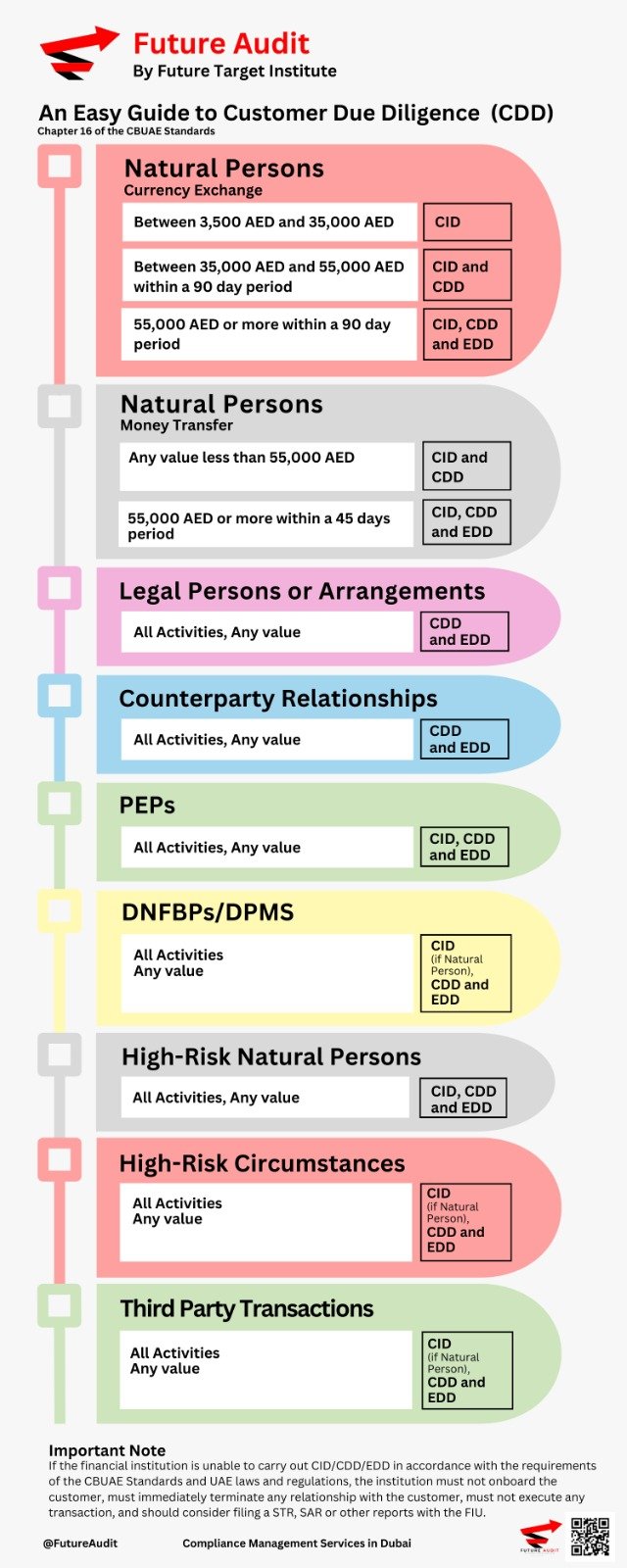
As per Article 21.2 of Cabinet Decision 74, Licensed Financial Institutions (LFIs) are required to:
Perform regular searches against applicable sanctions lists for customers, transactions, beneficial owners, and related entities.
Conduct continuous screening before executing transactions or establishing new business relationships.
Ensure sanctions screening systems are only as effective as the quality of customer and transaction data used.
Sanctions Screening Guidelines – UAE Central Bank
Key Components of a Strong Sanctions Screening Framework
1.A well-calibrated risk-based approach: LFIs must review and enhance screening frameworks regularly, especially after significant regulatory or business changes.
2.Robust training & risk awareness: Employees must be trained in sanctions screening policies, procedures, and financial crime risks.
3. Integration into a wider compliance strategy: Screening should be closely linked with AML and KYC measures to ensure data accuracy.
4. Active oversight & governance: Senior management and board members should actively monitor and enhancescreening systems, addressing inefficiencies and staff-related issues promptly.
5.Quality assurance: LFIs should implement regular audits and validation processes to ensure screening accuracy and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Step 4: Ensure Ongoing Compliance & Audits
- Perform Regular Sanctions Audits – Conduct internal reviews of your sanctions screening processes.
- Monitor Transactions for Red Flags – Identify suspicious transactions linked to high-risk jurisdictions or entities.
- Enhance Due Diligence on High-Risk Customers – Apply Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) for politically exposed persons (PEPs) and high-risk sectors.
- Use AI & Automation for Screening – Invest in AI-powered real-time transaction monitoring systems.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with sanctions screening obligations can result in:
Fines from AED 50,000 to AED 50 million
Freezing or suspension of business operations
Criminal liability for executives & compliance officers
Reputational damage & banking restrictions
UAE sanctions enforcement guidelines
Step 5: Register with EOCN & Subscribe to Sanctions Lists
Why Register with EOCN?
Registering with the Executive Office for Control & Non-Proliferation (EOCN) ensures businesses receive real-time updates on sanctioned individuals and entities, helping them stay compliant with UAE regulations.
How to Subscribe to the UAE Sanctions Lists:
1️⃣ Access the Executive Office’s Website
https://www.uaeiec.gov.ae/en-us/un-page
2️⃣ Navigate to “Sanctions List” in Quick Links
3️⃣ Click on Subscribe
4️⃣ Fill Out the Subscription Form
5️⃣ Submit & Receive Confirmation Email
Subscribers receive email notifications whenever updates occur on the UAE Local Terrorist List or the UN Consolidated List.
📧 For More Information, Contact: IEC@UAEIEC.GOV.AE


Final Thoughts
Sanctions screening is a non-negotiable compliance requirement in the UAE. Businesses must ensure real-time screening, accurate reporting, and continuous monitoring to prevent financial crime risks.
Need expert AML & sanctions compliance support? Future Compliance provides tailored compliance solutions to help businesses meet their obligations.
Follow us for more AML insights, free resources, and compliance updates.
What challenges do you face with sanctions screening? Share your thoughts in the comments! #SanctionsCompliance #AML #UAERegulations #FinancialCrimePrevention