Definition & Stages of Money Laundering
How Money Laundering Works
Money laundering is a financial crime where criminals hide illegally obtained funds to make them seem legitimate. One crucial part of this process is layering, which means moving money through different financial institutions and banking systems to avoid detection. By adding multiple layers of transactions, criminals make it harder to connect the initial source of money to its final destination. As a result, authorities struggle to track the actual source of the proceeds of crime.
The Three Stages of Money Laundering
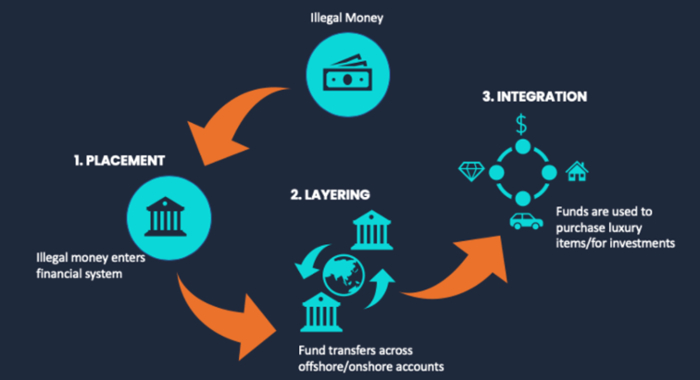
Money laundering happens in three stages: placement, layering, and integration. First, in the placement stage, criminals deposit illegal money into an account at a financial institution. Next, in the second stage, layering, they try to erase the money’s origin by moving money between different accounts or investing in assets. This stage creates multiple layers of ownership, sometimes involving legitimate owners, making it difficult for authorities to trace the actual source. Finally, during the integration stage, criminals withdraw and use the cleaned money without raising suspicion.
The Three Stages of Money Laundering Uncovered!
1. How Criminals Introduce Illegal Money into the Financial System
In the early stage of money laundering, called placement, criminals deposit illegal money into banks and financial institutions. They break large sums into smaller transactions to stay below the cash limit threshold and avoid scrutiny. Some use fake invoices or shell companies to make the funds seem legal. Others convert cash into negotiable instruments, such as checks or bonds, making detection more complex.
2. Hiding the Money Trail: The Layering Stage
During the second stage, known as layering, criminals move money across multiple accounts to erase its criminal source. They invest in stocks, securities, and liquid investments, making it harder to trace. Additionally, they use structuring by spreading transactions across different locations. Some even purchase luxury goods, jewellery, or precious metals to further hide their tracks.
3. Making Dirty Money Look Legal: The Integration Stage
At the third stage, called integration, the money is now clean and enters the legitimate economy. Criminals invest in real estate, open a business, or distribute money among partners-in-crime, friends, and associates. In terrorist financing, funds reach terrorist organizations to support unlawful activities. Without strong detection systems, these transactions blend into the financial system, fueling financial crime and harming the legal system.
The Hidden Risks of the Layering Process!
In the layering stage of money laundering, criminals try to hide criminal proceeds from their illegal activity. They move funds through different countries, making it harder for authorities to track the origin of the dirty money. To achieve this, they use structuring, breaking large amounts into smaller transactions that seem normal. Additionally, they invest in real estate, or convert cash into gold, casino chips, and other assets. These schemes help the money enter and leave different financial systems without raising suspicion.
To avoid detection, criminals use a series of transfers to spread money across the globe. They often set up fake businesses and anonymous accounts to further distance themselves from the money. The more layers they create, the harder it becomes to connect the money to its source. This method allows criminals to keep moving cash through various financial systems, avoiding legal consequences and continuing their criminal activity undetected.
Techniques & Methods Used in Layering
How Criminals Hide Illicit Funds
In financial crimes, criminals use various tactics to hide illicit funds and avoid detection by authorities. They transfer money through multiple accounts in financial institutions, making it harder to trace. Some criminals send money to offshore bank accounts or conduct international transfers to bypass strict regulations. Others invest in luxury cars, jewellery, or property to make their money appear legitimate. According to a report, nearly USD 2 trillion is laundered worldwide every year using these methods.
Use of Shell Companies and Trade-Based Money Laundering
Criminals often create shell companies in tax haven countries to launder money while remaining anonymous. These fake businesses issue bogus invoices and use dummy shipping documents to justify suspicious transactions. Additionally, trade-based money laundering allows criminals to overvalue or undervalue goods to move money undetected. Since these activities involve multiple jurisdictions, tracking the movement of money becomes a challenge for regulators.
Financial Transactions and Identity Concealment
To hide their identity, criminals use wire transfers, prepaid cards, and fund transfers between fake bank accounts. They rely on proxies and intermediaries to open legit accounts, making it difficult for investigators to trace the criminal activities. Many exploit KYC and customer due diligence loopholes to pass security checks undetected. By frequently transferring funds across accounts, they make it nearly impossible to identify the original source.
Laundering Money for Criminal Activities
Layering helps criminals finance illegal activities such as terrorism, purchasing arms, extortion, and the trade of banned drugs. Through black money, they support organisations engaged in crime while avoiding law enforcement. Without strong AML compliance and UBO identification, authorities struggle to detect and prevent such crimes. Governments must enforce stringent financial regulations to stop criminals from misusing the financial system for illegal gains.
The Dark Secrets of Structuring, Smurfing & Layering!
Smurfing is a known technique that criminals use to break down large financial transactions into multiple small transactions to avoid scrutiny. This layering technique helps them circumvent regulatory authorities and move money undetected. In the second stage of money laundering, a money launderer spreads illegal funds across different accounts in banks and financial institutions. Many also invest in jewellery items, precious metals, and high-value purchases to disguise their money. Smurfs specialize in structuring money transfers to stay below monetary thresholds, ensuring they do not raise suspicion.
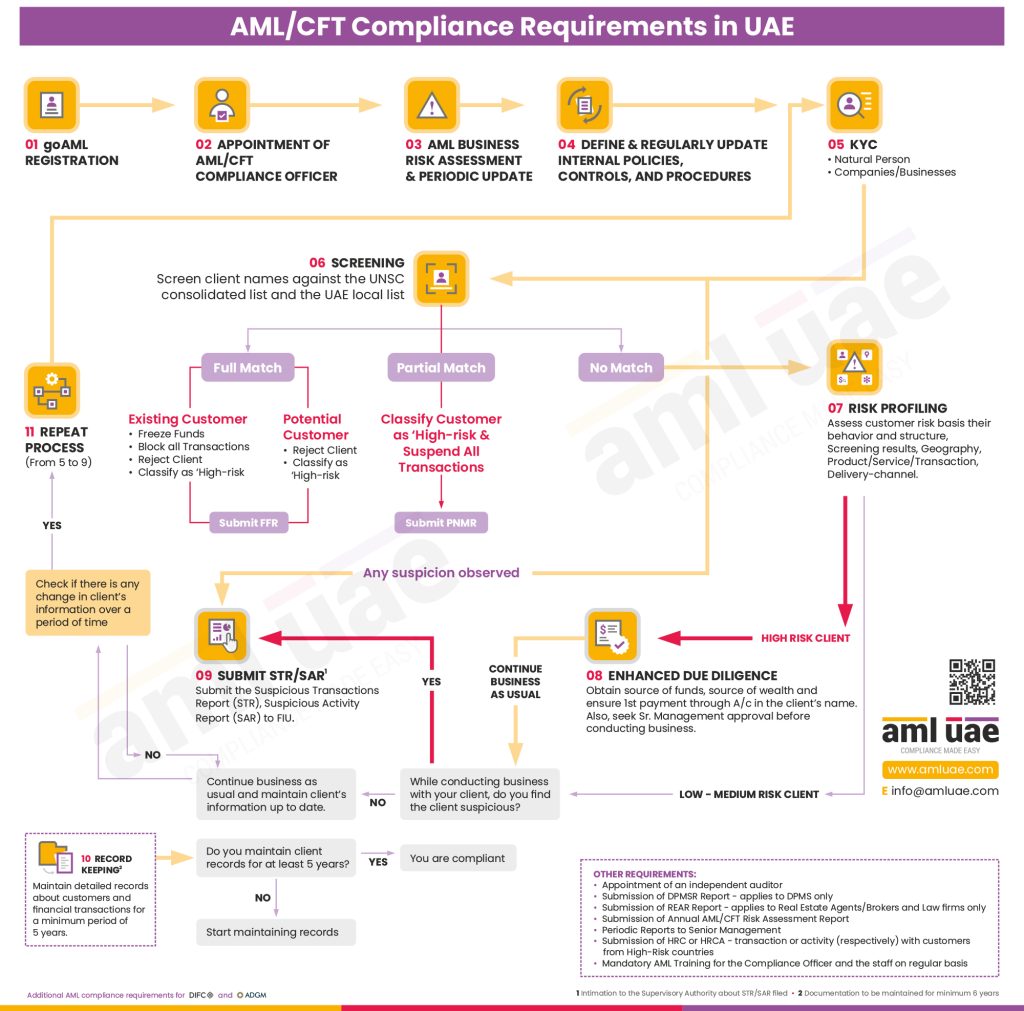
In countries like the UAE, AML authorities strictly enforce UAE AML Laws to fight money laundering. Any cash transactions above AED 55,000 in stones or other valuable assets must be reported through the goAML portal, which is managed by the FIU. To avoid this reporting threshold, criminals use structuring large amounts, breaking them into smaller purchases. They also manipulate regulatory thresholds to evade detection. Additionally, the Dealers in Precious Metals and Stones Report (DPMSR) requires businesses to meet filing requirements when handling large transactions. However, criminals have adopted new ways to stay hidden and operate under the radar of financial regulators.
The Tough Battle Against Layering in Money Laundering!
How Criminals Use Layering to Hide Money
Criminals use layering to make illegal money harder to identify by spreading it across multiple transactions and different financial institutions. They move cash into various bank accounts, often in a single bank, before sending it through wire transfers to high-risk geographies. This process helps hide the origin of funds and makes detection more challenging for law enforcement.
Common Red Flags of Layering in Money Laundering
- Large cash deposits made frequently across different banks to avoid suspicion.
- Immediate withdrawals after a fund transfer, making tracking more difficult.
- Quick succession of international transfers between unrelated parties to confuse authorities.
- Investing in real estate, luxury assets, or high-value goods like jewellery to legitimize funds.
- Reselling expensive assets through legitimate companies to create a clean transaction history.
- Using shell companies to hide the true ownership of assets.
- Depositing a huge volume of money from high-risk customers without clear business activity.
- Repeated rounded-off amounts in banking transactions, signaling potential structuring.
- Frequent movement of funds between institutions without any legitimate financial purpose.
- Purchasing assets under different names and locations to prevent direct tracking.
Critical Steps to Expose and Stop the Layering of Illegal Funds!
Identifying Suspicious Transactions and High-Risk Customers
To detect layering, financial institutions must apply robust KYC procedures. This involves identification and verification of customers, especially those linked to Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs) or listed on the sanctions list. Customer transactions should be monitored regularly to identify red flags such as unusual transfers, structured deposits, or frequent high-value transactions. Enhanced due diligence is essential for high-risk individuals, ensuring they do not exploit financial loopholes.
Strengthening AML Compliance to Prevent Laundering
Under UAE AML regulations, organizations must adopt stringent measures to stop financial crime and prevent criminals from laundering money. Ongoing transaction monitoring helps in detecting suspicious transactions linked to an artificial layer of fund movements. Effective screening of customers ensures early identification of those with a nexus to criminal activities. Additionally, documenting and reporting these risks help authorities take necessary action against individuals or organizations misusing financial systems.
Empowering Teams to Fight Financial Crime
A strong AML program requires continuous training for employees across different business segments. Proper onboarding ensures teams can recognize and prevent financial threats. A well-trained workforce creates a protective shielding system against illegal activities. Compliance officers must enforce comprehensive AML measures while keeping policies updated. Additionally, effective controls help deter criminals from moving dirty money through financial channels.
Urgent Need for AML Compliance!
To prevent money laundering, financial institutions and non-financial institutions must take a proactive approach and enforce a strong AML compliance framework. Organizations like FATF, MENAFATF, and the Egmont Group collaborate internationally with law enforcement agencies to detect and mitigate the movement of criminal proceeds linked to terrorist activities and financial crimes. Banks should actively monitor suspicious accounts, set deposit limits, and rely on technology for immediate alerts on high-risk transactions. Institutions must also maintain clear documentation, ensure strict identification, and apply strong controls to uncover layering and other suspicious activities.
Key AML Compliance Measures
- AML laws in the UAE require close monitoring of cash deposits and transactions that are withdrawn immediately to spot unusual behavior.
- DNFBPs and VASPs must conduct AML/CFT health check-ups to prevent financial abuse and illegal activities.
- Financial entities must implement AML/CFT policies and submit an Annual AML/CFT Risk Assessment Report for compliance verification.
- A vigilant eye on suspicious transactions helps identify and stop money laundering before it spreads further.
- Effective screening and real-time immediate alerts enable early detection of red flags in financial networks.
- Stopping crimes at local and international levels requires cooperation between authorities and financial watchdogs to enforce compliance.
Shocking Examples of Layering & Terrorist Financing!
Criminals use trade-based money laundering to move large amounts of cash through fake invoices and inflated prices, making illegal funds appear legitimate. They invest in real estate through shell companies and intermediaries to disguise the proceeds of crime and hide ownership details. Additionally, they use structuring transactions to break large amounts into smaller transactions, avoiding detection by authorities.
Many also rely on anonymous transactions in virtual currencies, which makes tracing funds difficult. Criminals further complicate investigations by engaging in complex financial transactions that blur the trail of illicit money. These tactics allow them to launder money while staying ahead of law enforcement efforts.
Layering in AML & Financial Crime
Layering is the second stage of money laundering, where criminals move illicit money through numerous transactions to hide its origin. They use wire transfers, fund transfers, and electronic transactions to shift money across financial institutions without raising suspicion. Some rely on alternative remittance systems, such as Hawala in the Middle East, Hundi in India, or Hui Kuan in Hong Kong, to transfer money outside of banking channels. Additionally, they use fake invoices, fraudulent transactions, and paper transactions to blur the document trail, making it harder for law enforcement to track their activities.
Common Layering Techniques in AML & Financial Crime
- Moving funds through different banking channels to complicate tracking efforts.
- Investing in securities, paintings, and antiques to disguise illicit gains.
- Using trusts and shell companies to hide ownership and make detection difficult.
- Conducting complex layering schemes to keep transactions untraceable.
- Exploiting non-traditional financial systems to avoid regulations.
- Splitting large amounts into smaller denominations to escape suspicion.
- Transferring money through foreign counterparts to sidestep local jurisdiction.
- Moving cash manually through covert means to avoid leaving an electronic record.
- Cycling money through multiple financial systems to make placement transactions appear legal.
By using these methods, criminals make the laundering process more challenging for AML investigators, making it critical for authorities to strengthen detection measures.
Technology & Institutional Approaches
Technology & Institutional Approaches
Financial institutions rely on cutting-edge tech and AI-driven technology to strengthen money laundering detection and prevent AML breaches. Advanced transaction monitoring helps track suspicious activities, such as human trafficking, drug trafficking, and green crime. Institutions use Know Your Customer (KYC) and screening technology to verify client identity and assess risk level. In the UK, over 460,000 SARs are filed annually, increasing the need for digital automation. The Covid-19 pandemic heightened financial crime risks, making holistic AML strategies essential to fight money laundering.
Institutional Strategies for AML Compliance
Organizations like the Egmont Group, FATF, and FIUs work with regulated institutions to strengthen AML regimes. The 2019 Economic Crime Plan focuses on reducing AML breaches and enforcing SARs reporting requirements. UK enforcement agencies enhance financial crime tracking and improve Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) processing. Legislative requirements ensure strict transaction monitoring, helping businesses follow compliance rules. A skilled team with strong expertise is crucial in preventing financial fraud.
The Role of Digitalisation in Anti-Financial Crime Efforts
With rising cases of layering, modern slavery, and Online Child Sex Abuse (CSAE), digitalisation plays a key role in combating crime. Napier and similar firms implement three core elements of AML—detection, reporting, and prevention—to strengthen compliance. STRs (Suspicious Transaction Reports) help report illegal activities, allowing law enforcement to act. Using technological advances, institutions can combat layering and stop criminals from misusing the financial system.
FAQs
1. What are the Three Stages of Money Laundering?
The Three Stages of Money Laundering include Placement, Layering, and Integration. Placement introduces illicit money into the financial system, Layering hides its source through multiple transactions, and Integration makes it appear legal.
2. What is the Second Stage of Money Laundering?
The Second Stage of Money Laundering is Layering, where criminals transfer money between financial institutions and use smaller amounts to avoid detection.
3. What is an Example of Layering in Money Laundering?
An Example of Layering is when Money Launderers move funds between countries, split transactions into smaller parts, or use regulated entities to disguise their source.
4. How do AML Rules Help Prevent Money Laundering?
AML rules enforce strict monitoring of suspicious transactions, requiring financial institutions to follow AML compliance policies and report illegal activities.
5. What is AML Compliance, and Why is it Important?
AML compliance includes regulations like AML/CFT policy and AML compliance services to detect and prevent money laundering in businesses and financial institutions.
6. Why is False-Positive Screening a Challenge in AML Compliance?
False-positive screening occurs when AML software flags legitimate transactions as suspicious, increasing workload for compliance departments and leading to unnecessary investigations.
7. What Role Do Professional AML Consultants Play?
Professional AML consultants assist businesses by providing AML training, AML health checks, procedures documentation, and in-house AML compliance solutions.
8. How Can Outdated Technology Affect AML Compliance?
Outdated technology makes sanctions compliance difficult, allowing criminals to bypass monitoring. Using leading AML consultants helps organizations stay updated.
9. What is the Role of Higher Management in AML Compliance?
Higher management must implement AML compliance services, enforce controls, and ensure proper AML software is used for monitoring.
10. How Does UAE Regulate Money Laundering?
The UAE enforces AML compliance policies through strict laws, requiring financial institutions to report suspicious transactions and follow sanctions compliance rules.