





AML/CFT Risk Assessment UAE Report: A Complete Guide
Introduction
The Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Combating the Financing of Terrorism (CFT) Risk Assessment in the UAE is a crucial process for ensuring financial security and regulatory compliance. Given the UAE’s status as a global financial hub, strict AML/CFT regulations are in place to prevent illicit financial activities and align with Financial Action Task Force (FATF) standards.
💡 Why is AML/CFT Risk Assessment Important?
✔ Prevents financial crimes like money laundering and terrorist financing
✔ Helps businesses remain compliant with UAE laws
✔ Avoids hefty fines and legal repercussions
✔ Strengthens the UAE’s reputation as a transparent financial market
Regulatory Framework for AML/CFT in the UAE
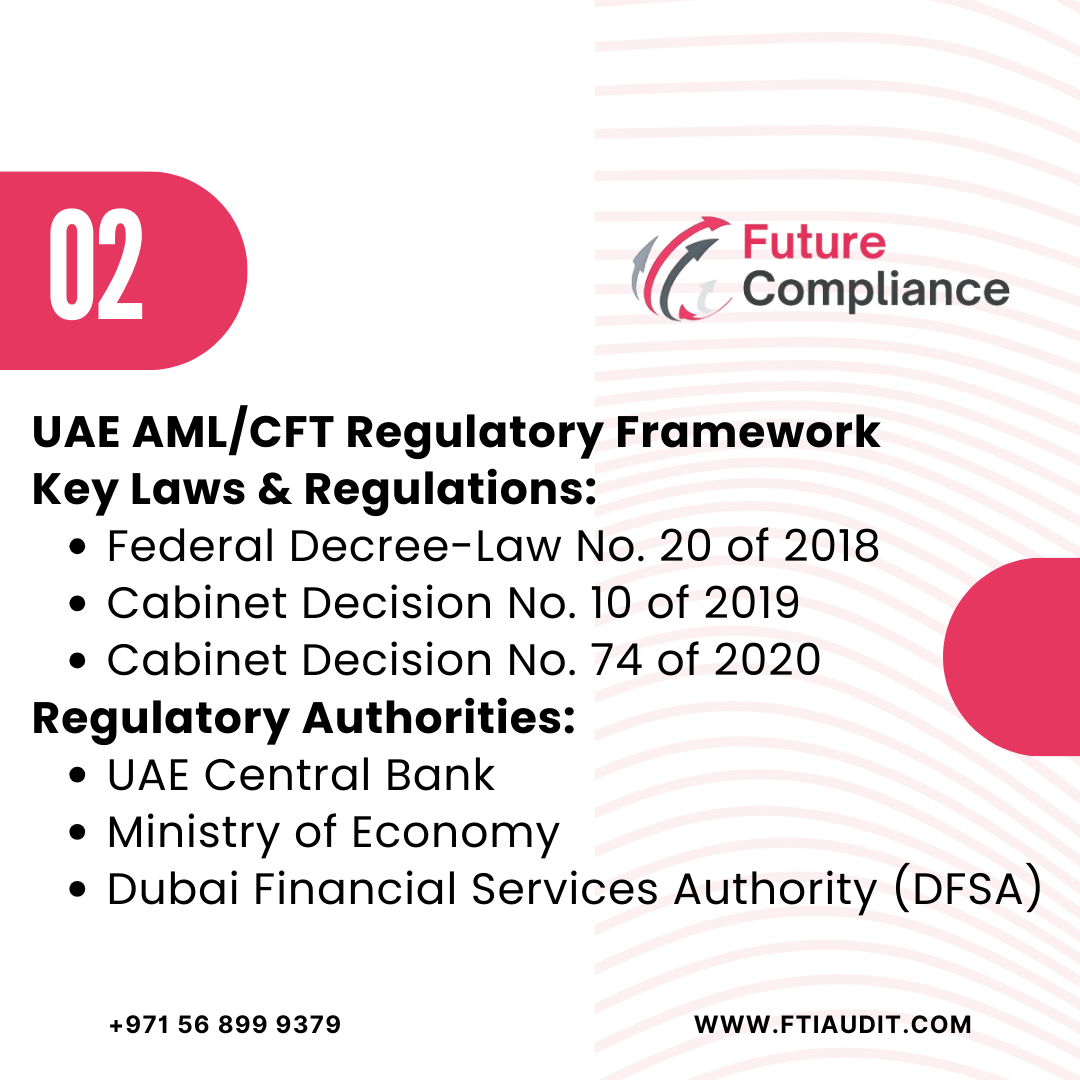
The UAE’s AML/CFT framework is governed by key laws and regulatory bodies:
Key Regulations
- Federal Decree-Law No. 20 of 2018 – Establishes AML/CFT obligations for financial institutions and DNFBPs.
- Cabinet Decision No. 10 of 2019 – Provides executive regulations and risk-based compliance strategies.
- Cabinet Decision No. 74 of 2020 – Strengthens enforcement mechanisms and penalties.
Key Regulatory Authorities
- UAE Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU) – Analyzes and reports suspicious transactions.
- UAE Central Bank – Supervises financial institutions for AML compliance.
- Ministry of Economy UAE – Regulates DNFBPs, including real estate brokers, lawyers, and dealers in precious metals and stones.
- Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA) – Ensures AML compliance in DIFC.
- Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM) – Supervises financial entities within ADGM.
📢 Tip: Stay updated with UAE’s AML laws by following FATF’s UAE Mutual Evaluation Report.
What is an AML/CFT Risk Assessment?
An AML/CFT risk assessment evaluates financial transactions, customers, and business activities to identify vulnerabilities and implement risk mitigation strategies.
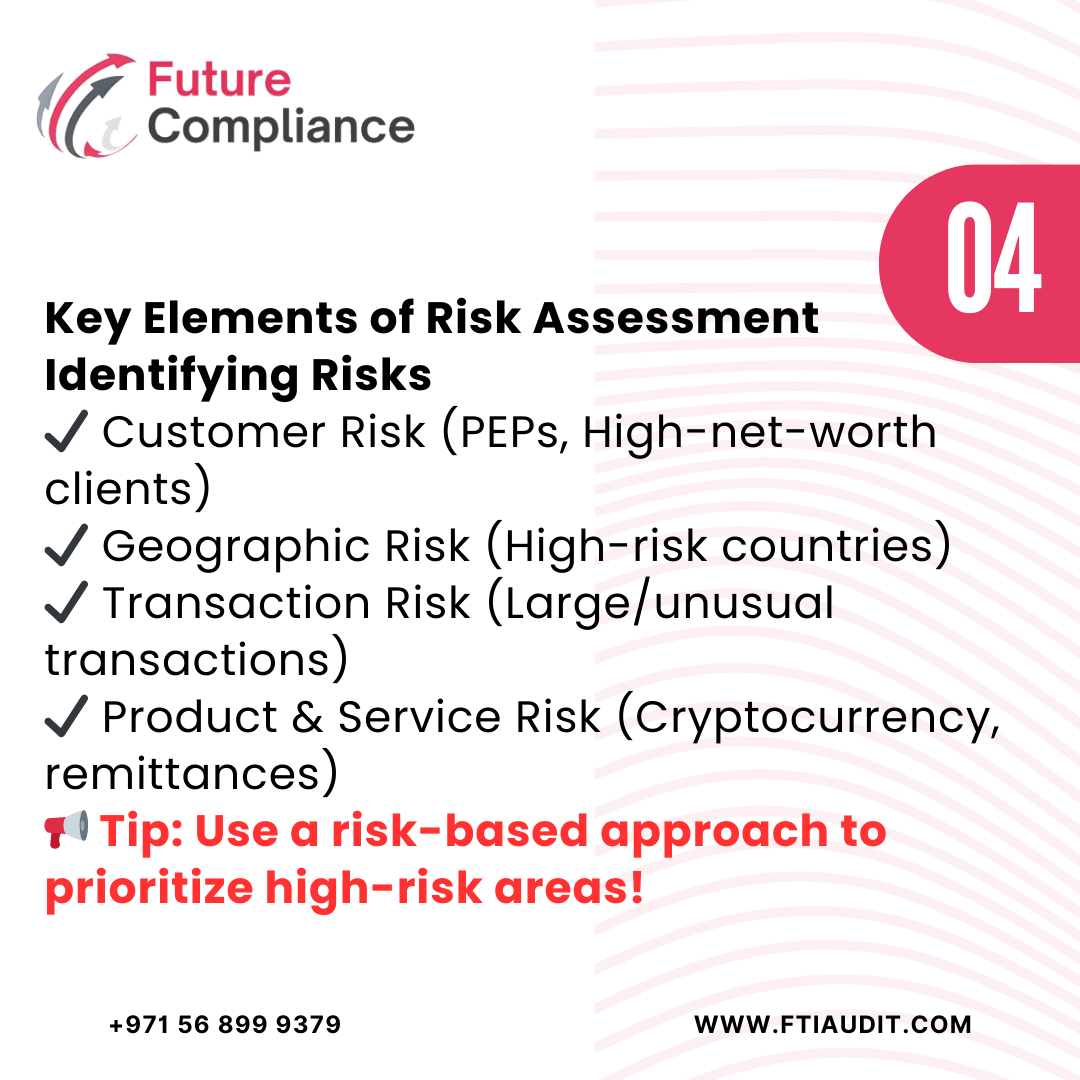
🔍 Key Elements of AML/CFT Risk Assessment
🔹 Customer Risk – Assessing high-risk customers, including Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs).
🔹 Geographic Risk – Identifying risks associated with high-risk jurisdictions as per FATF’s High-Risk Countries List.
🔹 Transaction Risk – Monitoring large, complex, or unusual transactions to prevent money laundering activities.
🔹 Product and Service Risk – Reviewing financial services prone to terrorist financing, such as cryptocurrency and cross-border payments.
📢 Tip: Use World Bank’s AML/CFT Risk Guidelines to develop a global compliance strategy.
Annual AML/CFT Risk Assessment Report in UAE
Who Must File the Report?
All Designated Non-Financial Businesses and Professions (DNFBPs) in the UAE must submit an Annual AML/CFT Risk Assessment Report to the Ministry of Economy (MOE).
Legal Requirement
As per Article 44(1) of Cabinet Decision No. 10 of 2019, all DNFBPs are legally required to file an annual AML/CFT report.
DNFBPs That Must Submit AML Reports:
✔ Real estate agents & brokers
✔ Dealers in precious metals & stones
✔ Auditors & accountants
✔ Legal professionals & corporate service providers
📢 Tip: Use the goAML Platform to report suspicious activities and submit compliance filings.
How to File the AML/CFT Risk Assessment Report?
Step 1: Collect Required Information
The report requires submission of:
✔ Inherent Risk – Customer, product, and geographic risks.
✔ Controls & Risk Mitigation – Internal policies and compliance measures.
✔ Business Operations – Entity structure, transactions, and risk management strategies.
Step 2: Complete the AML/CFT Survey Questionnaire
The survey questionnaire includes:
🔹 Business structure details (ownership, parent company, licensing authority)
🔹 Customer verification process (PEPs, non-resident customers, legal persons)
🔹 Number of AML/CFT compliance violations (if any)
🔹 Transaction monitoring and reporting framework
📢 Tip: Download UAE’s Annual AML/CFT Report Guide for a step-by-step submission process.
Step 3: Submit to the Ministry of Economy
All reports must be filed within the prescribed deadline to avoid penalties.
📢 Need Help? FTI Audit provides professional assistance in AML report filing to ensure compliance.
Risk-Based Approach for AML Compliance
The Ministry of Economy applies a risk-based approach to AML/CFT compliance, requiring businesses to prioritize high-risk areas.
Best Practices for AML/CFT Compliance
✔ Conduct Regular Risk Assessments – Align with IMF’s AML/CFT Compliance Framework.
✔ Implement Strong Internal Controls – Use Wolfsberg Group’s AML Principles for compliance best practices.
✔ Train Employees on AML Compliance – Provide staff with FATF’s Training Modules.
✔ Use Advanced Transaction Monitoring Tools – Leverage AI-driven AML software to detect suspicious transactions.
📢 Tip: Stay updated with United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) reports on emerging money laundering risks.
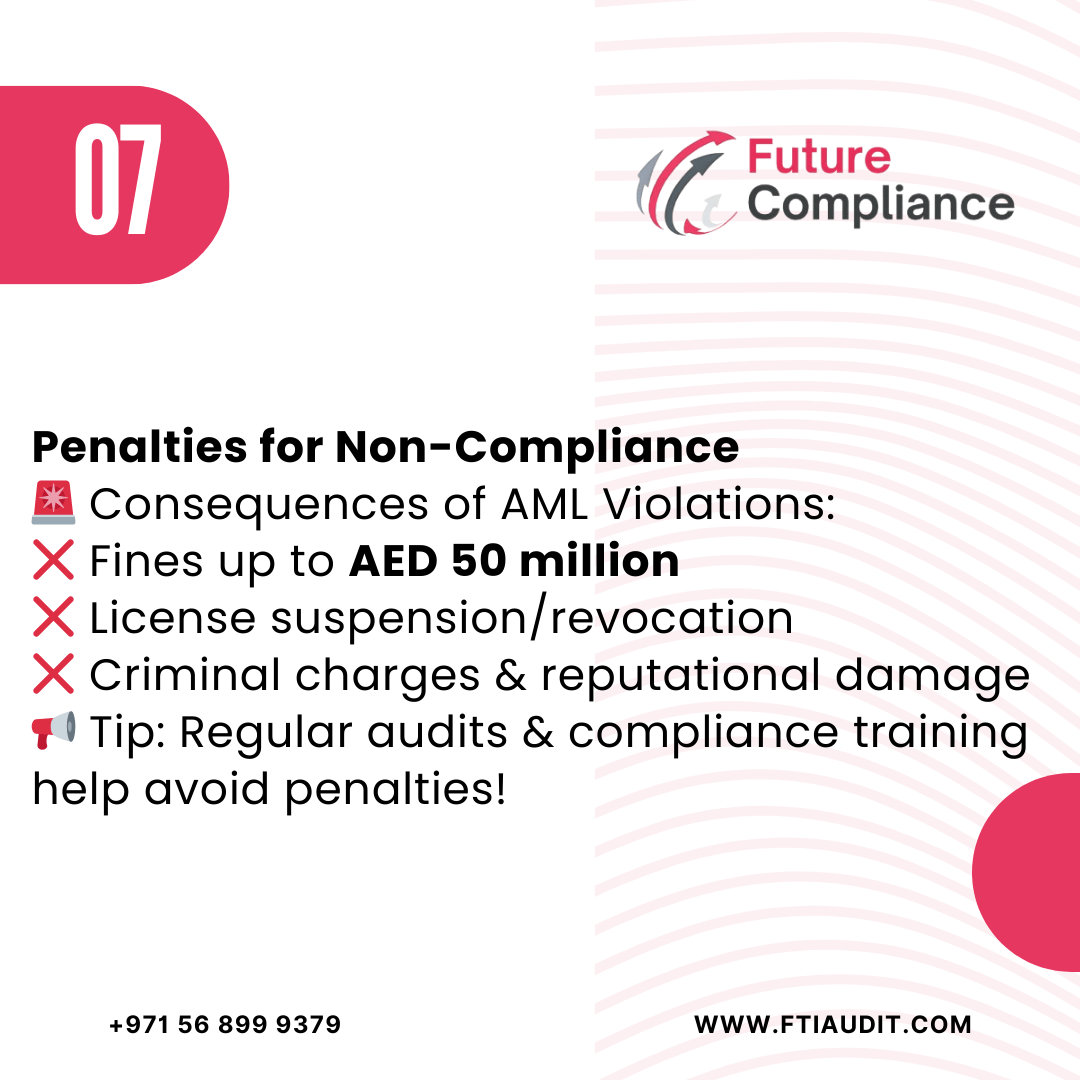
Penalties for Non-Compliance
🚨 Failure to comply with AML regulations in the UAE can result in:
❌ Fines up to AED 50 million
❌ License suspension or revocation
❌ Criminal prosecution and reputational damage
💡 Need Compliance Support? FTI Audit offers AML consulting, risk assessments, and compliance solutions to protect your business.
Conclusion
The AML/CFT Risk Assessment UAE Report is essential for businesses to avoid financial crime risks and ensure regulatory compliance. By implementing a risk-based AML framework, organizations can:
✔ Strengthen their compliance measures
✔ Avoid legal penalties
✔ Build trust with financial regulators
📢 Stay compliant with UAE AML laws. Contact FTI Audit today for expert assistance!